Energy is the capacity to make things happen
or, as scientists put it,‘work’. It takes many
forms. Heat energy boils water. Chemical
energy fuels cars and aeroplanes. Electrical
energy drives all kinds of small machines and
keeps lights glowing.
Energy is one of the most fundamental parts of our universe. We use energy to do work. Energy lights our cities. Energy powers our vehicles, trains, planes and rockets. Energy warms our homes,cooks our food, plays our music, gives us pictures on television. Energy powers machinery in factories and tractors on a farm.
Energy from the sun gives us light during the day. It dries our clothes when they’re hanging outside on a clothes line. It helps plants grow. Energy stored in plants is eaten by animals, giving them energy. And predator animals eat their prey, which gives the predator animal energy.
Everything we do is connected to energy in one form or another.
Energy is defined as: “the ability to do work.”Fossil Fuels
There are three major forms of fossil fuels: coal, oil and natural gas. All three were formed many hundreds of millions of years ago, even before the time of dinosaurs – hence the name fossil fuels. The age they were formed is called the Carboniferous Period. It was part of the Paleozoic Era. “Carboniferous” gets its name from carbon, the basic element in coal and other fossil fuels When burned, fossil fuels release energy, which is used to generate power. Fossil fuels are non-renewable energy sources because they will eventually run out.
About 20 per cent of the world’s energy is generated from coal and its use is increasing.
About 60 per cent of the world’s energy comes from oil and natural gas. Oil is the main fuel used in transportation, and both oil and gas are burned to produce heat.
In 1960, it was estimated that existing underground fossil fuels would last for about 40 years. By 1990, more reserves had been found, but the rate at which they were being used had increased. In 1990, the reserves were still estimated to last about 40 years.
Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources are those that will not run out in the foreseeable future. Most “renewables” are cleaner and less harmful to the environment than fossil fuels. They are made from resources Mother Nature will replace, like wind, water and sunshine.
Wind Power
The process of using wind to create electricity has been
around for a long time. When the wind turns the blades
of a windmill, it spins a turbine inside a small generator
to produce electricity, just like a big coal power plant. Scientists estimate that by 2030, wind power could provide more than 10 per cent of the world’s electricity.
Solar Power
Have you ever used a magnifying glass to make something
melt or burn? You were using solar power! The Sun is a non-polluting source of renewable energy. “Solar” is the Latin word for “sun” - and it’s a powerful source of energy. In fact, the sunlight that shines on the Earth in just one hour could meet world energy demand for an entire year!
We can use solar power in two different ways: as a
heat source, and as an energy source. People have used
the sun as a heat source for thousands of years.
Families in ancient Greece built their homes to get the
most sunlight during the cold winter months. In the 1830s, explorer John Herschel used a solar collector to cook food during an adventure in Africa. You can even try this at home!
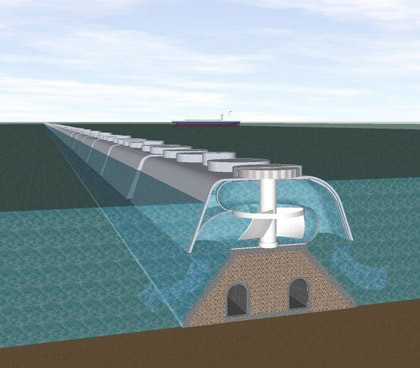
Tidal Power
Tidal power is generated at barrages built across estuaries. As the tide rises or falls, water is kept at high or low tide level inside the barrage. When the water level differs by about 10ft, water flows through huge turbines.
Hydroelectric Power
“Hydro” means “water” in Latin - so “hydro power” is
made from water. It is generated at dams and waterfalls.
Falling water drives turbines, which in turn drive
electricity generators. About 7 per cent of the world’s
energy is provided by hydroelectricity.
Geothermal Energy
“Geo” means “from the earth,” and “thermal” means “heat,” so this type of energy is found under the earth. It is generated by heat energy in the Earth’s crust. At present, most geothermal energy is generated in volcanically active regions, such as Iceland and New
Zealand.
Biomass Energy
Have you ever sat by a campfire or fireplace? If so, you’ve see biomass energy in action!
Biomass means “natural material.” So, biomass energy is derived from organic matter. Biomass energy uses natural materials like trees and plants to make electricity. It can also mean waste products like trash. They produce less air pollution and do not usually contribute to global warming.
Nuclear Energy
Another major form of energy is nuclear energy, the energy that is trapped inside each atom. One of the laws of the universe is that matter and energy can’t be created nor destroyed. But they can be changed in form. Nuclear energy is generated by the breakdown of uranium and plutonium atoms. Nuclear power stations do not emit polluting gases or contribute to global warming, but accidents and the disposal of fuel rods pose serious risks. Matter can be changed into energy. The famous scientist Albert Einstein, created the mathematical formula that explains this. This equation says: E=mc2 E is energy, m is mass, and c is the speed of light. Scientists used Einstein’s famous equation as the key to unlock atomic energy and also create atomic bombs. The negetive and most challenging aspect of nuclear energy is that its waste remains dangerously radioactive for thousands of years, and has therefore
to be buried deep underground or at sea.
Subscribe to Child Project Helper by Email